VIDAS® NEPHROCHECK® [TIMP-2 · IGFBP-7]
Aid in the risk assessment for moderate or severe acute kidney injury.
The VIDAS NEPHROCHECK assay is intended to be used in conjunction with clinical evaluation in patients who currently have or have had within the past 24 hours acute cardiovascular and or respiratory compromise and are ICU patients as an aid in the risk assessment for moderate or severe acute kidney injury (AKI) within 12 hours of patient assessment. The VIDAS NEPHROCHECK test is intended to be used in patients 21 years of age or older.
The VIDAS NEPHROCHECK test is an automated test for use on the VIDAS 3 instrument.
About Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
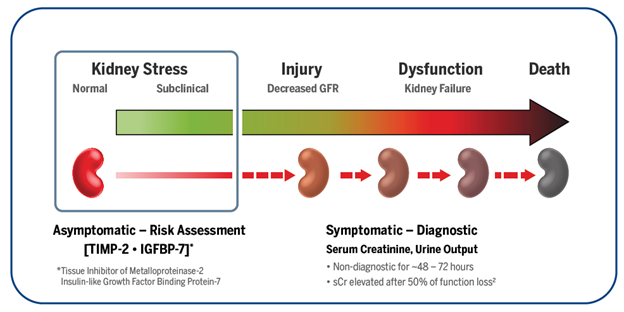
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is an abrupt decrease in kidney function. It is a syndrome that is defined by a rapid increase in serum creatinine, decrease in urine output or both.
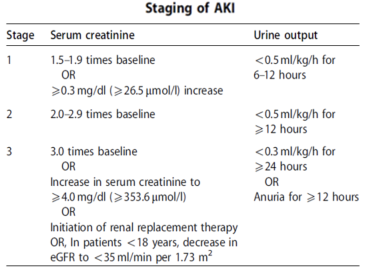
The KDIGO (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes) has recommended a staging system for the severity of AKI.
According to KDIGO there are 3 stages of AKI. The table below shows the different classification criteria for each stage.1
There are different causes of AKI. Some conditions can be linked to specific kidney disease, like glomerulonephritis and decreased kidney perfusion, for example. However, AKI can be, also, caused by conditions like sepsis, use of nephrotoxic drugs or circulatory shock. Sepsis accounts for 50% of AKI cases and is the most common cause of AKI in critically ill patients.2
AKI is considered an economic and public health burden as:
- up to 50% of critically ill patients develop some stage of AKI3
- AKI increases the hospital length of stay by 1 to 3 days4
- patients with AKI have 9 times more risk to develop chronic kidney disease (CKD)5
References
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Inter, Suppl. 2012; 2:1-138.
- Rashid Alobaidi, MD, Rajit K. Basu, MD, Stuart L. Goldstein, MD, and Sean M. Bagshaw, MD, MSc. Semin Nephrol. 2015 January; 35(1):2-11.
- Mandelbaum T. Crit Care Med. 2011;39(12):2659-2664.
- Dasta JF, et al. Costs and outcomes of acute kidney injury (AKI) following cardiac surgery. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23(6):1970-1974.
- Heung M. Steffickk DE.. Zivin K, et al. Acute Kidney injury recovery pattern and subsequent risk of CKD: an analysis of Veterans Health Administration data. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016:67(5):742-752
Overview
VIDAS NEPHROCHECK is FDA-cleared to aid clinicians in the risk assessment of moderate to severe acute kidney injury (AKI) within 12 hours of patient assessment. When used in conjunction with clinical evaluation, early information is provided so that clinicians may either rule out kidney stress with confidence, or implement a series of protective measures for the kidneys.
VIDAS NEPHROCHECK combines a one-step sandwich assay with two detection steps carried out successively to detect biomarkers of acute kidney injury, TIMP-2 and IGFBP-7. The test provides results in ~46 minutes.
The single-use Solid Phase Receptable (SPR) serves as the solid phase as well as the pipetting device. Reagents for the assay are ready-to-use and pre-dispensed in the sealed single-use strips. All of the assay steps are performed automatically by the VIDAS 3 instrument.
The sample is transferred into the well containing anti-IGFBP-7 and anti-TIMP-2 antibodies with alkaline phosphatase (conjugate). The sample/conjugate mixture cycles in and out of the SPR device several times. This operation enables the two proteins to bind with the immunoglobulins that are fixed to the interior wall of the SPR device and to the conjugate to form a sandwich.
For each protein, the intensity of the fluorescence is proportional to the concentration in the sample. At the end of the assay, the protein concentrations are calculated by the VIDAS 3 instrument in relation to the two calibration curves, one corresponding to each protein, and encoded in the Master Lot Entry (MLE) data. The concentration from each protein, TIMP-2 and IGFBP-7, is converted into a single numerical result called the AKIRISK™ Score.
Kit Content
SPR Device
 The interior of the SPR device is coated during production with anti-IGFBP-7 and anti-TIMP-2 monoclonal antibodies (mouse). Each SPR device is identified by the “NEPH” code. Only remove the required number of SPR devices from the pouch and carefully reseal the pouch after opening.
The interior of the SPR device is coated during production with anti-IGFBP-7 and anti-TIMP-2 monoclonal antibodies (mouse). Each SPR device is identified by the “NEPH” code. Only remove the required number of SPR devices from the pouch and carefully reseal the pouch after opening.
Reagent Strip
 The strip consists of 10 wells containing diethanolamine and sodium azide covered with a labeled foil seal. The label comprises of a barcode that indicates the assay code, lot number, and expiration date. The foil of the first well is perforated to facilitate the introduction of the sample. The last well of each strip is a cuvette where the fluorometric reading is performed. The wells in the center section of the strip contain the various reagents required for the assay.
The strip consists of 10 wells containing diethanolamine and sodium azide covered with a labeled foil seal. The label comprises of a barcode that indicates the assay code, lot number, and expiration date. The foil of the first well is perforated to facilitate the introduction of the sample. The last well of each strip is a cuvette where the fluorometric reading is performed. The wells in the center section of the strip contain the various reagents required for the assay.
S1 Calibrator
 Buffer containing proteins + stabilizer of animal orgin + preservative.
Buffer containing proteins + stabilizer of animal orgin + preservative.
Specs
|
Sample Stability (Urine Supernatant) |
5 hours at room temperature 24 hours refrigerated 6 months frozen, 2 freeze/thaw cycles |
| Sample Type and Prep | Urine Sample. Centrifuge: 10 minutes at 1000 x g at +2°C / +25°C (35.6°F - 77°F) |
| Sample Loading |
Automated on-board pipetting of sample or manual |
| Processing Time | 46 minutes |
| Throughput |
Up to 12 tests at a time |
| LIS Connection | Bidirectional |
| Quality Control |
Controls can be run day of use concurrently with patient tests |
| Electronic Quality Control | None |
| Calibration |
Calibration performed with each new lot or every 56 days |
| System Footprint |
24” L x 29.5” W x 25.2” H |